The Stages of Gum Disease: Periodontal Health Information
 Gum disease can lead to a whole host of dental problems, including the loss of gum tissue and tooth loss. While it's estimated that 47 percent of American adults suffer from some form of gum disease, many do not understand the nature of the condition.
Gum disease can lead to a whole host of dental problems, including the loss of gum tissue and tooth loss. While it's estimated that 47 percent of American adults suffer from some form of gum disease, many do not understand the nature of the condition.
The team at our Orland Park practice offers state-of-the-art dental services, designed to address all sorts of issues that may impact your oral hygiene. Let's take a moment to consider the progression of gum disease and what can be done to remedy the problem.
The Basics: What Is Gum Disease?
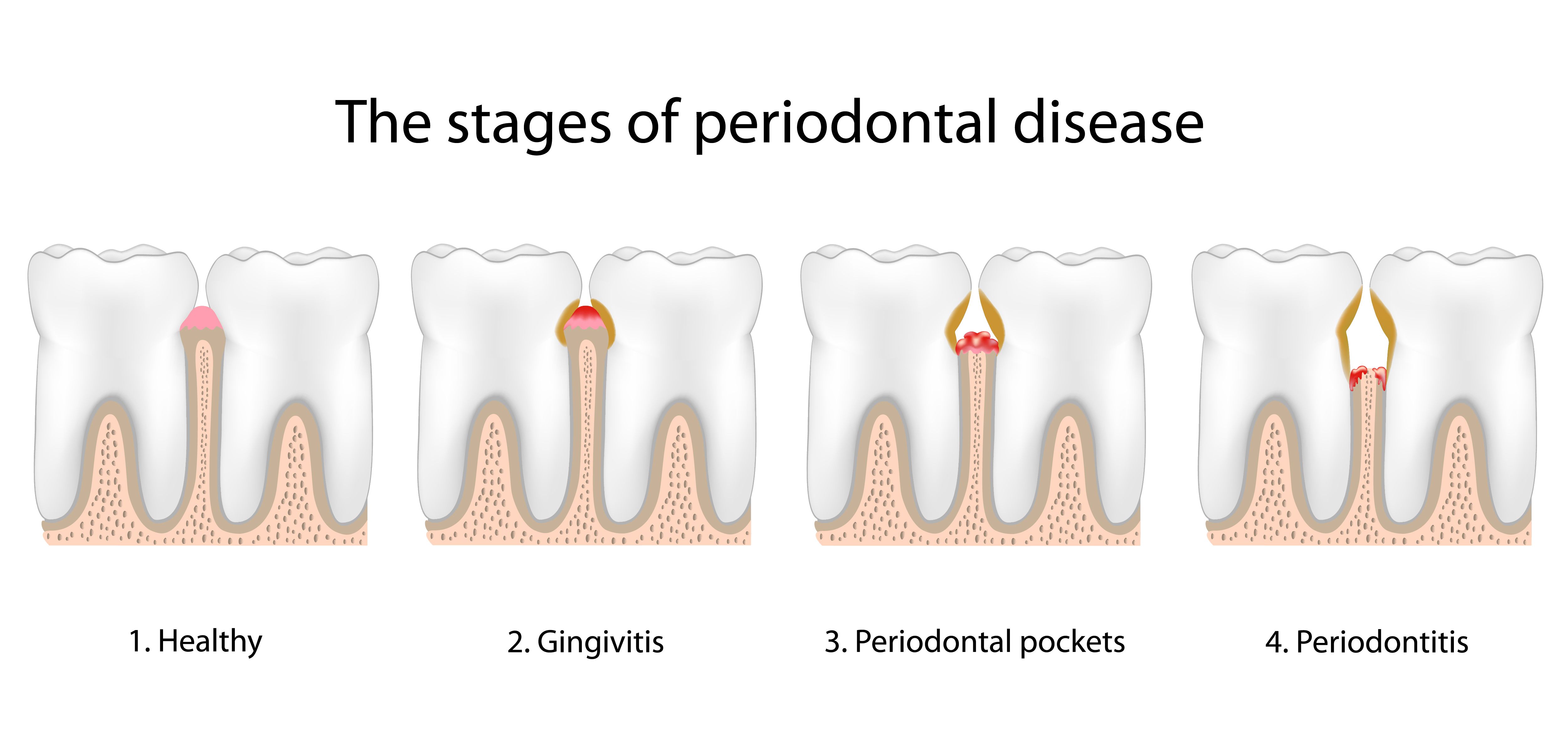
Gum disease is a bacterial infection of the gum tissue. It is caused by the same bacteria that causes tooth decay and bad breath. There are three different stages of gum disease, and each stage involves a worsening of the previous symptoms. These three stages are:
- Gingivitis
- Periodontitis
- Advanced periodontitis
Let's explore each of these stages of gum disease in greater detail below.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease. During this stage of the condition, patients typically notice an irritation of the gums and the gumline. Discoloration of the gums is also common, as is some bleeding along the gumline.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is the next stage of gum disease. At this point, patients may notice more severe symptoms than gingivitis. This could mean worse discoloration of the gums, swelling of the gums, a strange taste in the mouth, and chronic bad breath. Gum recession may also occur during this stage, which is the loss of gum tissue along the gumline and the exposure of the root structure of the teeth. Teeth may also start to shift and feel loose given the damage to the gumline.
Advanced Periodontitis
In the most advanced stages of gum disease, patients will experience significant issues with the health and appearance of their gums. Teeth may be shifted significantly out of position, or even fall out by this point. Serious swelling and inflammation may affect large portions of the gumline. Oral abscesses may also be present, which can be dangerous if they rupture.
Treatments for Gum Disease
When treating gum disease, it's important to get the infection under control. For gingivitis, this typically involves the use of antiseptic medications as well as deep cleaning (root planing and scaling). For periodontitis and advanced periodontitis, these treatments may be combined with the use of antibiotics and the removal of severely damaged gum tissue. Gum grafting can be performed to rebuild the damaged gumline.
Dentists will also work to address any damage done to the teeth and the other structure of the mouth. This means using dental restorations to address decay and various kinds of dental appliances to address tooth loss.
Tips for Preventing Gum Disease
To prevent gum disease from developing, consider these oral hygiene tips:
- Avoid using tobacco products
- Eat a healthy and well-balanced diet
- Stay hydrated by drinking water
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day (ideally after every meal)
- Floss your teeth at least once a night (ideally after every meal)
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups
Learn More About Treating Gum Disease
For more information about gum disease and how dentists can help you achieve a healthier and more beautiful smile, it's important that you contact our advanced dental care center today. Our team looks forward to your visit and discussing your options for lasting dental wellness.


